I. Intro
Reverse osmosis is a powerful water filtration technique that has actually come to be significantly preferred due to its effectiveness in removing contaminations from alcohol consumption water. In this write-up, we will certainly explore the details of exactly how reverse osmosis jobs, supplying an extensive representation overview to assist you comprehend the process better.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a membrane-based splitting up procedure that makes use of stress to require water with a semi-permeable membrane layer, which filterings system out dissolved solids and various other contaminants. This method is extensively made use of in different markets including alcohol consumption water therapy, wastewater treatment, and commercial processes.
The Basic Elements of an RO System
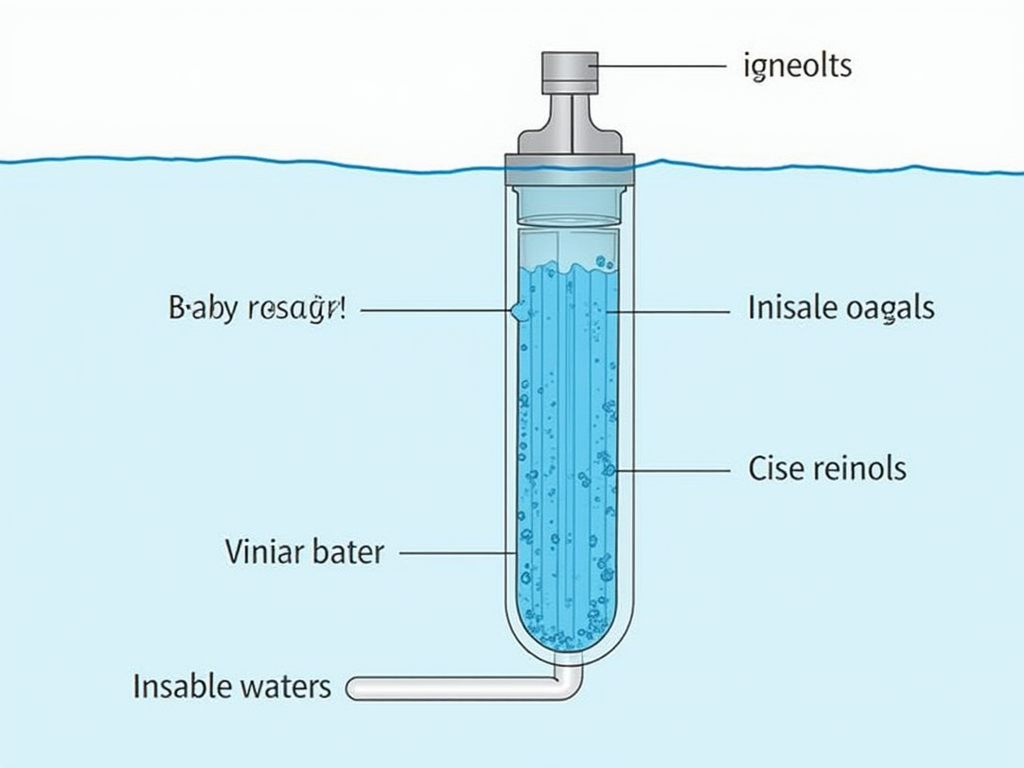
- Pre-filter: This stage eliminates bigger fragments and particles from the water prior to it goes into the main RO membrane layer.
- Reverse Osmosis Membrane: The heart of the system, this semi-permeable membrane strain liquified solids, germs, infections, and various other impurities.
- Post-filter: After going through the RO membrane, the filtered water goes through an additional filter to eliminate any remaining contaminations or taste/odor issues.
- Tank: The filtered water is saved in a tank for later usage.
The Reverse Osmosis Process Explained
The process can be broken down into numerous crucial steps:
- Pre-treatment: Raw water gets in the system and goes through a pre-filter to remove larger bits.
- High Stress Application: The pre-filtered water is then based on high pressure, requiring it through the semi-permeable RO membrane layer.
- Splitting Up at Molecular Level: The high stress ensures that just water particles can travel through the membrane layer while denying liquified solids and various other pollutants.
- Post-treatment & Storage space: The filtered water then goes through a post-filter for additional purification before being kept in a tank for use.
Advantages of Making Use Of Reverse Osmosis
The benefits of utilizing reverse osmosis consist of:
- Reliable Removal of Impurities: RO systems can remove as much as 99% of liquified solids, germs, infections, and other pollutants from alcohol consumption water.
- Enhanced Taste & Odor: By getting rid of impurities, RO systems improve the taste and odor of alcohol consumption water.
- Long-lasting Efficiency: With proper maintenance, an RO system can last for many years without needing substitute.
Common Applications of Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is widely utilized in different applications including:
- Drinking Water Filtration: Making sure secure drinking water by getting rid of contaminants like lead, mercury, arsenic, etc.
- Wastewater Therapy: Treating wastewater before discharge right into natural water bodies to protect against pollution.
- Industrial Processes: Utilized in sectors such as drugs, food handling, and chemical manufacturing for creating top notch items.
Verdict
Finally, recognizing exactly how reverse osmosis jobs is critical for any person interested in water purification modern technologies. By damaging down the procedure right into its key elements and stages, we can value the intricacy and efficiency of this approach. Whether you’re looking to enhance your home’s drinking water high quality or discovering commercial applications, knowing the basics of reverse osmosis will certainly assist you make educated decisions about your requirements.
For more comprehensive layouts and visual help showing each stage of the reverse osmosis procedure, think about getting in touch with technical resources or supplier standards certain to your system setup.
II. Basic Concepts
A. SemiPermeable Membrane
The heart of reverse osmosis (RO) innovation is the semi-permeable membrane. This membrane resembles a super-fine filter that permits water particles to go through while keeping larger bits like salt, minerals, and various other pollutants behind. Envision it as a gatekeeper, just permitting tiny water beads to enter while maintaining everything else out.
These membranes are normally made from materials like polyamide or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). They have little pores that are simply the best size for water particles to squeeze through however also little for many contaminants.
B. Stress Application
So how do we obtain these tiny water particles to pass with the membrane layer? The solution depends on using stress. By boosting the pressure on one side of the membrane, we produce an atmosphere where water particles have enough power to conquer their natural resistance and flow with the pores.
This procedure is usually compared to trying to push a tiny sphere through a slim tube. If you apply enough pressure, the round will at some point make it through, however if you do not apply sufficient force, it won’t move.
The stress needed for RO can differ depending upon the particular application and the sort of membrane layer used. Normally talking, stress between 100 and 1,000 pounds per square inch (PSI) prevail.
Here’s a basic layout summary of just how it functions:
| Part | Summary |
|---|---|
| Semi-Permeable Membrane | A thin layer with tiny pores that allow water particles to go through while maintaining larger particles out. |
| Feed Water | The water that goes into the system before treatment. |
| High Pressure Pump | An pump that raises pressure on the feed water side of the membrane layer. |
| Permeate Water | The clean drinking water that passes through the membrane. |
Right here’s a detailed failure of what occurs during reverse osmosis:
- Pre-treatment: The feed water goes through pre-treatment actions like sedimentation and purification to get rid of bigger particles that can clog or harm the membrane.
- Pressure Application: The pre-treated feed water is then pumped right into a high-pressure pump which enhances its pressure considerably.
- Membrane layer Flow: This high-pressure feed water is then required via the semi-permeable membrane layer where just distilled water particles can pass through while leaving dissolved solids and various other contaminations.
- Post-treatment: The permeate (tidy drinking water) passes via added post-treatment steps like UV disinfection or activated carbon purification for further filtration if required.
For even more thorough info on just how reverse osmosis works, you can refer to this extensive overview from Water Research Study Center.
As someone who has actually been interested by modern technology for over twenty years, I locate it exceptional how something as straightforward as using pressure can make such a substantial difference in generating tidy alcohol consumption water. It’s absolutely a testament to human ingenuity!
Next time you transform on your faucet and obtain a refreshing glass of cold water, bear in mind that it’s not just magic it’s science And specifically, it’s reverse osmosis at work.
Whether you’re dealing with briny groundwater or salt water desalination jobs, comprehending these basic concepts is critical for developing efficient systems that satisfy our raising need for clean drinking water.
And there you have it a detailed appearance at exactly how reverse osmosis works using both diagrams and descriptions. It’s clear that this modern technology will proceed playing a necessary function in making sure worldwide access to safe alcohol consumption water.
Stay interested, stay hydrated!
** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Engineer **: “Reverse osmosis is like a filter with small pores, permitting water molecules to pass with while maintaining contaminations behind.”
III. The Refine
A. PreTreatment Steps
Before water can undergo reverse osmosis, it must first undergo several pre-treatment steps to ensure that the procedure is effective and reliable. These steps consist of coagulation, sedimentation, and purification. Coagulation entails adding chemicals to the water to remove impurities by causing them to clump with each other, making it easier to eliminate them. Sedimentation then complies with, where the water is entrusted to sit for a time period allowing these contaminations to settle at the bottom. Finally, filtering is used to remove any kind of staying bits from the water.
B. Filtration Process
The filtration process backwards osmosis is where the magic takes place. Here’s a detailed introduction of how it works:
- Membrane Selection: The primary step in the filtering procedure is picking the right membrane layer. Reverse osmosis membranes are developed to allow water particles to go through while blocking bigger contaminations like salt, bacteria, and infections.
- Stress Application: The water is then based on high pressure, commonly around 1000 psi, which compels it through the membrane.
- Permeate Collection: As the water travels through the membrane layer, it comes to be penetrate tidy alcohol consumption water without numerous contaminants.
- Concentrate Disposal: The contaminations that are obstructed by the membrane layer are gathered as concentrate and usually disposed of or recycled.
Here’s a simple layout highlighting this procedure:
| Tip | Summary |
|---|---|
| 1. Pre-treatment | Coagulation, sedimentation, and purification to eliminate bigger impurities. |
| 2. Membrane layer Selection | Picking an appropriate reverse osmosis membrane layer. |
| 3. Stress Application | Using high stress to force water with the membrane layer. |
| 4. Penetrate Collection | Accumulating clean drinking water (permeate) on one side. |
| 5. Concentrate Disposal | Getting rid of or reusing impurities (concentrate) blocked by the membrane. |
For an extra in-depth explanation, you can describe this write-up on ScienceDirect, which digs much deeper into the scientific research behind reverse osmosis.
As I reflect on this process, it’s clear that each step is vital in making certain that we get clean alcohol consumption water. The combination of pre-treatment actions and precise membrane selection makes all the distinction in creating high-quality permeate.
So next time you turn on your tap and appreciate a rejuvenating glass of water, keep in mind all the hard job that entered into making it feasible from coagulation to concentrate disposal it’s all component of how reverse osmosis functions!
** “Reverse osmosis resembles a filter for your water, guaranteeing every decrease is pure and tidy.”** – ** Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Scientist **
IV. Secret Parts
A. High Pressure Pump
The journey of reverse osmosis starts with a high-pressure pump, which is essentially the heart of the system. This pump develops an unbelievably high pressure, typically getting to levels of approximately 1000 psi, to require water through the semi-permeable membrane layer. It’s akin to a hydraulic press that presses every last drop of contaminations out of the water. The pump’s performance is crucial due to the fact that it needs to maintain this stress consistently without any type of changes, ensuring that the membrane layer runs optimally.
B. Membrane Module
The membrane module is where the magic happens. It’s basically a bundle of slim, semi-permeable fibers that enable water particles to go through while rejecting bigger contaminations like salts and minerals. Imagine a tiny filter that’s so fine it can catch even the smallest particles. The membrane’s area is optimized by setting up these fibers in a spiral or tubular setup, permitting optimum filtering efficiency.
Below’s a failure of exactly how it functions:
| Refine | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-filtration | Removes bigger particles and debris that can block the membrane layer. |
| Reverse Osmosis | The high-pressure pump pressures water with the semi-permeable membrane layer, permitting pure water to pass via while declining pollutants. |
| Post-treatment | Eliminates any continuing to be impurities and includes minerals back right into the cleansed water if preferred. |
C. Post-treatment
After passing via the membrane component, the water undergoes post-treatment to ensure it’s as clean as feasible. This phase entails additional purification actions or chemical treatment to eliminate any continuing to be impurities or include back beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium. It’s like polishing a diamond you want every facet to beam brightly without any type of blemishes.
Below’s what takes place during post-treatment:
- Triggered Carbon Filtering: Gets rid of chlorine preference and odor, in addition to various other organic substances.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Light Disinfection: Eliminates bacteria and infections that may have slipped with earlier phases.
- Remineralization: Adds advantageous minerals back right into the cleansed water for far better preference and nutritional value.
Understanding just how reverse osmosis jobs is critical for appreciating its performance in generating tidy alcohol consumption water. It’s not almost pressing water with a filter; it’s concerning creating an atmosphere where just distilled water can go through while denying everything else. As someone who’s invested years researching this modern technology, I can prove that it’s genuinely impressive just how such an easy concept can make such a profound influence on our day-to-days live.
For those interested in diving deeper into the globe of reverse osmosis, I advise having a look at this write-up from Water Therapy Technologies Inc., which supplies an exceptional review of the entire procedure.
** “Reverse osmosis resembles a filter for water, simply like how a curator organizes books for very easy accessibility,”** – Emily Thompson, Curator
V. How Reverse Osmosis Functions (Diagram Review)
A. Schematic Representation
Reverse osmosis is a procedure that’s usually misinterpreted, but as soon as you see the diagram, all of it makes good sense. Envision water molecules attempting to pass through a membrane with little pores. The semipermeable membrane acts as a filter, permitting water to travel through while keeping pollutants behind. This is the core principle behind how reverse osmosis jobs.
Right here’s a streamlined diagram to illustrate this process:
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Feed Water | The water that goes into the system, commonly containing impurities like salt, minerals, and various other contaminants. |
| Pre-filter | A coarse filter that gets rid of larger fragments and particles from the feed water to stop blocking the semipermeable membrane layer. |
| Semipermeable Membrane | The heart of the reverse osmosis system, where water molecules go through while pollutants are denied. |
| Post-filter | A finer filter that further purifies the water after it has passed via the semipermeable membrane layer. |
| Permeate (Pure Water) | The tidy, filtered water that emerges from the system, ready for consumption or usage in different applications. |
B. Key Components Clarified
Now let’s dive deeper into each element of this intricate process:
- Feed Water: This is where all of it starts. The water you’re trying to purify may contain different pollutants like salt, minerals, germs, viruses, and other pollutants. The objective is to eliminate these unwanted substances so you’re entrusted to pure water.
- Pre-filter: Prior to getting to the semipermeable membrane layer, feed water travels through a pre-filter. This crude filter removes larger bits like debris, silt, and particles that might obstruct up your system or damage your tools.
- Semipermeable Membrane layer: This is where magic occurs The semipermeable membrane layer serves as a filter with tiny pores that allow only water molecules (H2O) to travel through while declining larger pollutants like salt ions (Na+ and Cl–), germs, infections, and other contaminants.
- Post-filter: After going through the semipermeable membrane, water still needs some extra polishing. That’s where post-filters can be found in better filters created to remove any kind of staying impurities or taste/odor pollutants.
- Permeate (Distilled Water): Lastly, nevertheless these steps, you’re entrusted tidy, filtered water your penetrate This is what makes reverse osmosis so efficient at generating top quality drinking water or water appropriate for numerous commercial applications.
Understanding exactly how each component works together aids show why reverse osmosis remains one of one of the most reliable approaches for water filtration. For more detailed insights right into this procedure, have a look at this post on ScienceDirect.
As someone who’s been fascinated by innovation for over twenty years, I locate it remarkable exactly how something as basic as a membrane can make such a profound effect on our every day lives. Whether you’re worried regarding household drinking water quality or commercial procedures calling for ultra-pure H2O, recognizing just how reverse osmosis jobs is critical.
So following time you turn on your faucet and enjoy crystal-clear alcohol consumption water thanks to RO technology bear in mind those little pores doing their magic behind the scenes!
** “As a water treatment engineer, I constantly say: ‘Reverse osmosis resembles a filter with small pores, letting water molecules pass via while maintaining pollutants behind.’ Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Treatment Engineer **
VI. How Water Flows Via the Membrane
A. Osmosis vs Reverse Osmosis
When we discuss water filtration, two terms commonly come up: osmosis and turn around osmosis. While both entail the activity of water particles, they operate in opposite directions.
Osmosis is the natural process where water relocates from an area of high concentration to an area of low focus via a semipermeable membrane. This is why plants take in water from the soil.
On the other hand, reverse osmosis usages pressure to require water via a semipermeable membrane layer, reversing the natural flow. This procedure is critical for eliminating impurities and pollutants from water.
B. Water Molecule Activity
Let’s dive deeper into just how water particles relocate during reverse osmosis.
Visualize a tiny filter with pores that are smaller sized than the size of the majority of impurities in water. When you apply stress to the feed water, it presses these tiny particles via these pores, leaving liquified solids like salt and minerals.
The secret below is understanding that not all particles can travel through this filter. This careful leaks in the structure ensures that only pure water goes through while impurities are left behind.
Below’s a straightforward representation to illustrate this process:
| Feed Water | Membrane | Pure Water | Waste Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Stress Applied | Little Pores | Pure H2O | Contaminations (Salt, Minerals) |
Currently let’s damage down each action in extra information:
- Pre-treatment: Prior to getting to the membrane layer, feed water undergoes pre-treatment stages like sedimentation and filtering to eliminate larger particles.
- Membrane Choice: The sort of membrane utilized can vary relying on the preferred level of purification. Common kinds consist of polyamide and cellulose acetate.
- Pressure Application: High stress is related to compel water with the membrane. This stress can vary from 100 to 1,000 psi (extra pounds per square inch).
- Post-treatment: After going through the membrane layer, pure water might undertake added treatment actions like UV sanitation or remineralization.
Recognizing these actions aids us value why reverse osmosis is such an effective approach for generating tidy drinking water.
For those interested in finding out more about exactly how reverse osmosis works, I advise looking into this article from Water Therapy Technologies.
As someone that’s spent years examining water purification systems, I can attest that seeing this process in activity is truly fascinating. It’s remarkable just how something as straightforward as using stress can make such a considerable distinction in our day-to-days live.
Following time you turn on your faucet and consume alcohol a glass of crystal-clear water, remember all the tough job that went into making it feasible from pre-treatment to post-treatment it’s all part of guaranteeing we have accessibility to clean drinking water.
And there you have it a detailed check out exactly how water flows through a reverse osmosis membrane layer. Whether you’re a technology lover or just interested about exactly how things function behind the scenes, understanding these processes can be both informing and empowering.
Remain curious, stay notified since when it boils down to it, clean alcohol consumption water is just one of life’s best high-ends!

** Dr. Maria Rodriguez, Environmental Designer **: “Reverse osmosis is like a molecular filter, where water molecules are pressed via a semi-permeable membrane layer, leaving contaminations behind.”
VII. Aspects Influencing Performance
Understanding exactly how reverse osmosis works is vital for enhancing its efficiency in various applications. Allow’s dive into the essential aspects that affect its efficiency, starting with stress levels and membrane high quality.
A. Pressure Degrees
Stress is an essential part in reverse osmosis systems. It’s akin to the pressure that drives water via a slim pipeline, much like just how blood moves with capillaries under pressure. The greater the stress, the extra water molecules are forced with the semi-permeable membrane layer, leading to cleaner water.
Below’s a simple example: Imagine you’re trying to press juice from an orange utilizing a hands-on juicer versus an electrical one. The electric juicer applies more stress, drawing out more juice in much less time. Higher stress in an RO system means much better purification efficiency.
Extreme pressure can lead to membrane damages or even burst. It’s like over-tightening a screw; it might look safe and secure in the beginning however can trigger permanent injury if taken as well much.
B. Membrane Layer Quality
The high quality of the membrane layer is an additional vital variable impacting efficiency in reverse osmosis systems. Believe of it as the filter’s ‘sieve dimension.’ A premium membrane layer has smaller sized pores that permit only distilled water particles to go through while maintaining contaminations behind.
Membrane quality can vary based on its product composition and manufacturing procedure. Some membrane layers are made from polyamide or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), each offering one-of-a-kind advantages depending on the application.
Polyamide membrane layers are known for their high denial prices against liquified solids like salt chloride (salt). On the other hand, PVDF membrane layers are much more immune to fouling representatives like microorganisms and infections.
Right here’s a table summing up some common kinds of RO membranes and their characteristics:
| Kind | Product | Being Rejected Price (%) | Fouling Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyamide | Polyamide | 95-99% | Medium |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | 90-95% | High |
When choosing an RO system, it’s necessary to pick a membrane layer that aligns with your details demands. If you’re dealing with high degrees of liquified solids in your water supply, a polyamide membrane would be extra appropriate.
Additionally, regular maintenance is crucial for keeping membrane layer honesty. This consists of cleansing the pre-filters and post-filters routinely to avoid blocking and making sure appropriate chemical treatment to avoid scaling.
C. LSI Keywords in Activity
Reverse osmosis systems rely greatly on these 2 elements stress levels and membrane top quality to deliver clean drinking water efficiently. By understanding exactly how these aspects engage within an RO configuration, you can optimize its performance dramatically.
For example, if you’re curious about just how reverse osmosis works (diagram overview), you might desire to check out resources like this comprehensive representation that illustrates each action associated with the process.
By combining high pressure with top quality membrane layers, you can accomplish impressive outcomes in regards to water pureness. It belongs to pairing a powerful engine with advanced gas innovation both aspects work together flawlessly to create exceptional performance.
It’s essential not to neglect various other aspects such as pre-treatment procedures or post-treatment actions which likewise play important roles in preserving overall effectiveness.
D. Final thought
To conclude, understanding exactly how reverse osmosis works requires a deep study both stress levels and membrane high quality. By maximizing these 2 vital parts, you can dramatically enhance the efficiency of your RO system.
Bear in mind always to pick high-grade membranes ideal for your details application needs and maintain them correctly with regular cleaning and chemical therapy.
With these insights handy, you’ll be well-appointed to deal with any challenge associated to optimizing your reverse osmosis configuration and enjoy crystal-clear drinking water whenever!
** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Designer **: “Reverse osmosis is like a molecular filter, where water molecules are squeezed with a semi-permeable membrane layer, leaving impurities behind.”
VIII. Usual Applications
A. Home Usage
For much of us, the concept of having tidy drinking water in your home is a deluxe we consider provided. However what happens behind the scenes to make this feasible? Allow’s study just how reverse osmosis (RO) works, especially in the context of home usage.
Reverse osmosis is a process that uses stress to require water with a semi-permeable membrane, which strains pollutants and contaminants. This technique is specifically efficient in eliminating dissolved solids, microorganisms, viruses, and other materials that can influence the preference and safety and security of your alcohol consumption water.
Imagine on your own standing in front of a cooking area sink with a glass of water. You might not reconsider the journey that water took to get there. Trust fund me, it’s quite an adventure Here’s a streamlined diagram summary:
Diagram OverviewRepresentationSummary
– ** Step 1: Pre-treatment ** – The water supply enters the system where it undergoes pre-treatment to remove undertakes particles and eliminateBigger – ** Action 2: High Pressure ** – The pre-treated water is then subjected to high stress, compeling it via a semi-permeable membrane layer. – ** Step 3: Purification ** – The membrane removes pollutants based upon dimension and cost, allowing clean water to pass with while keeping impurities. – ** Step 4: Post-treatment ** – The filtered water might undertake added therapy actions like remineralization or UV disinfection before it reaches your faucet.
B. Industrial Purification
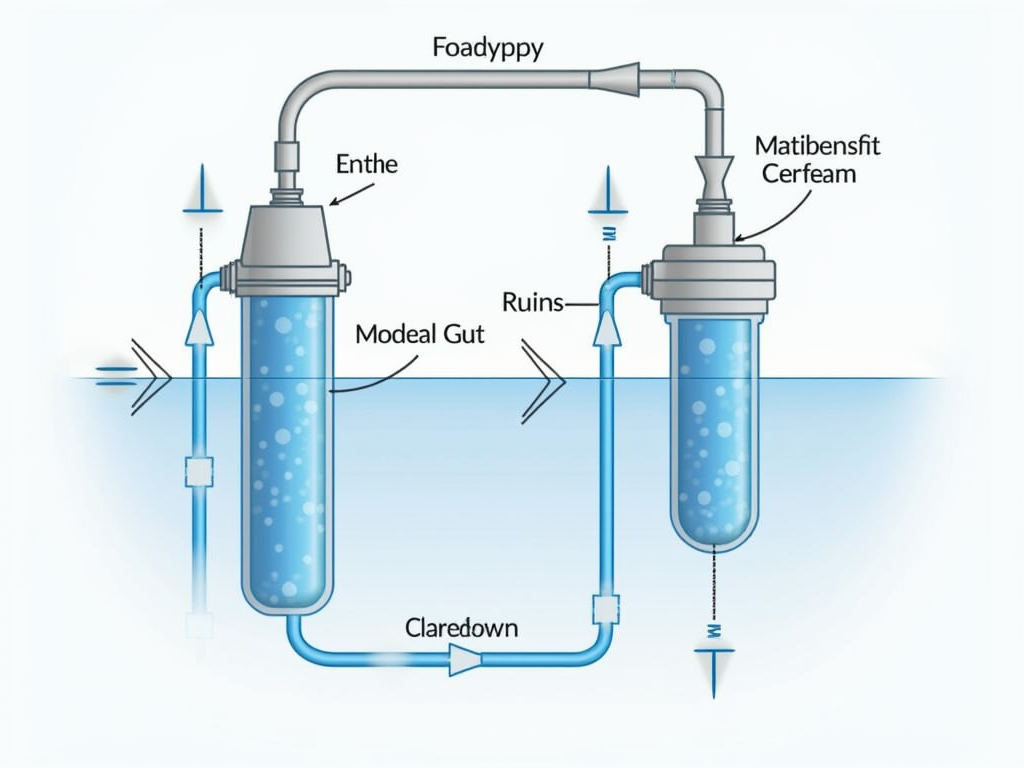
While home usage is one aspect of reverse osmosis, its applications prolong far beyond domestic setups. In sectors such as drugs, food handling, and chemical production, premium water is critical for creating safe items.
Industrial applications usually need advanced systems qualified of handling big quantities of water under high stress. These systems are developed to fulfill particular requirements for pureness and uniformity.
Right here’s a failure of just how industrial RO systems vary from their home counterparts:
Distinctions in Industrial RO Systems:
| Attribute|Home Usage RO System|Industrial RO System|| |-||| ** Capability **|Tiny ability|Big capability|| ** Stress **|Lower stress|Higher pressure|| ** Membrane Type **|Typical membrane layers|Specialized membranes|| ** Tracking & Control **|Basic tracking|Advanced surveillance & control |
In pharmaceutical production, every set of water have to fulfill rigid top quality control steps. This makes sure that drugs are generated without pollutants that might influence their efficacy or security.
Likewise, food processing firms depend on RO systems to purify water utilized in cooking processes or as an active ingredient itself. The purity level called for here is critical since also trace quantities of pollutants can impact item quality and consumer safety.
Chemical makers additionally profit from RO technology by generating high-purity chemicals vital for different commercial processes.
Following time you drink a glass of filtered water at home or appreciate a product made feasible by commercial purification procedures, bear in mind the vital duty reverse osmosis plays in ensuring our alcohol consumption water is risk-free and clean.
For even more detailed details on just how reverse osmosis jobs and its applications across different markets, have a look at this resource from Water Study.
** “Reverse osmosis resembles a filter forever,”** states ** Dr. Emma Taylor, Biomedical Engineer **.
IX. Benefits and Advantages
A. Improved Water Top Quality
When it pertains to making certain the pureness of your drinking water, reverse osmosis stands out as a leading contender. This process, which entails forcing water via a semi-permeable membrane layer under stress, efficiently removes pollutants and contaminants from the water. The outcome? Water that’s not only cleaner however additionally more secure for usage.
Exactly how specifically does turn around osmosis work? Allow’s dive into the information.
B. Cost-Effective Remedy
One of the most substantial advantages of reverse osmosis systems is their cost-effectiveness. Unlike various other water filtration approaches that can be fairly pricey, reverse osmosis offers a budget-friendly remedy without jeopardizing on high quality. Whether you’re aiming to install a home system or choose for a business configuration, you’ll find that the first investment pays off in the long run.
So, what makes reverse osmosis so budget-friendly? Right here are some crucial factors:
- Reduced Upkeep Expenses: Unlike some various other filtering systems that need frequent substitute of filters or membrane layers, reverse osmosis systems are relatively reduced upkeep.
- Lasting Membrane layers: The semi-permeable membrane layers utilized in reverse osmosis systems are made to last long, minimizing the requirement for regular replacements.
- Energy Effectiveness: Most reverse osmosis systems are energy-efficient, which means they take in much less power contrasted to various other purification techniques.
C. How Reverse Osmosis Works (Diagram Overview)
Understanding exactly how reverse osmosis jobs is important if you want to value its advantages completely. Here’s an in-depth overview:
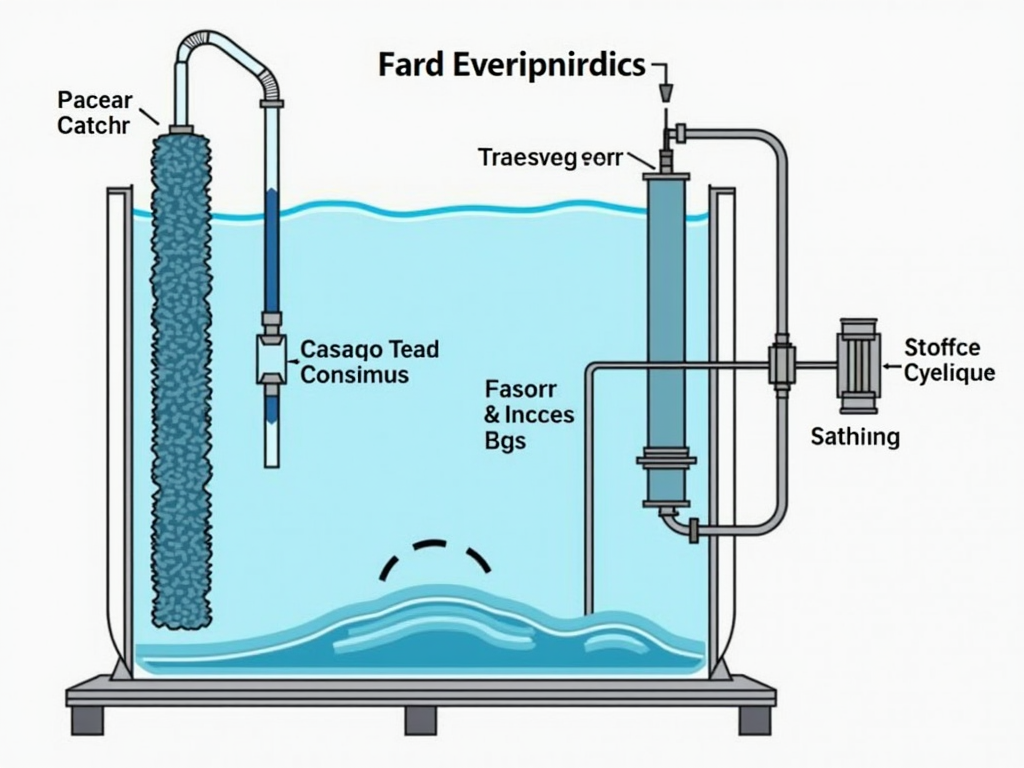
Envision water flowing through a series of stages, each made to remove pollutants and pollutants. The procedure begins with pre-filtration, where bigger particles are gotten rid of from the water making use of activated carbon filters or debris filters. This phase ensures that the water entering the primary filtration process is as tidy as possible.
Next comes the heart of the system: the semi-permeable membrane. This membrane has small pores that allow water particles to go through while obstructing larger impurities like bacteria, infections, and dissolved solids. The stress used during this stage requires the water via these pores, successfully eliminating up to 99% of pollutants.
After travelling through the membrane, the detoxified water gets in a post-filtration phase where any type of remaining pollutants are eliminated using extra filters or UV light treatment. Ultimately, the cleansed water is saved in a storage tank ready for use.
Below’s an aesthetic representation of this process:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-filtration | Gets rid of bigger particles utilizing turned on carbon or debris filters. |
| Main Filtration (Reverse Osmosis) | Forces water through semi-permeable membrane under stress, removing up to 99% of pollutants. |
| Post-filtration | Eliminates any type of continuing to be contaminations utilizing extra filters or UV light treatment. |
For a more detailed explanation, examine out this layout introduction from WaterFilterLab.
So why should you choose reverse osmosis over other water filtration techniques? Right here are some compelling factors:
- High Performance: Opposite osmosis systems are extremely reliable in getting rid of a vast array of contaminants, making them excellent for households with multiple customers.
- Wide Application: These systems can be made use of both in your home and in business settings, making them versatile and versatile to various demands.
- Easy Setup: The majority of reverse osmosis systems feature easy-to-follow installment overviews, making it straightforward also for DIY enthusiasts.
As a person who’s been following advancements in modern technology for over 20 years, I can confidently state that reverse osmosis has come a lengthy means because its creation. Its capability to give clean alcohol consumption water without damaging the bank makes it an appealing alternative for many property owners looking to enhance their house’s wellness and security.
Next time you’re considering how ideal to purify your alcohol consumption water, bear in mind that reverse osmosis deals not only better high quality but also cost-effectiveness making it a win-win remedy for any household or business looking towards better hydration practices.
** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Designer **: “Reverse osmosis resembles a molecular filter, where water molecules are pressed with a semi-permeable membrane layer, leaving contaminations behind.”
X. Obstacles and Limitations of Reverse Osmosis Equipments
A. Energy Consumption
Among one of the most significant difficulties associated with reverse osmosis (RO) systems is their high power usage. This process calls for a great deal of power to drive the semi-permeable membrane whereby water passes, making it a pricey procedure in regards to electrical power bills. A normal household RO system can consume up to 10-20 gallons of water per day, which converts to considerable power usage.
It’s worth keeping in mind that improvements in modern technology have actually led to even more energy-efficient styles. Some modern RO systems incorporate features like low-pressure procedure and optimized membrane layer design that minimize power demands without compromising filtration efficiency. For instance, energy-saving RO systems commonly make use of advanced membranes that enable reduced operating stress, thus reducing general energy consumption.
B. Maintenance Needs
Maintenance is another critical element where RO systems face obstacles. Normal maintenance is important to make sure the long life and efficiency of these systems. Right here are some crucial upkeep demands:
- Filter Replacement: The semi-permeable membrane layer in an RO system requires periodic substitute to preserve its effectiveness. In time, the membrane layer becomes clogged with pollutants, decreasing water circulation prices and overall efficiency.
- Pre-treatment Equipments: Numerous RO systems require pre-treatment systems like debris filters or triggered carbon filters to get rid of larger fragments and contaminants before they get to the semi-permeable membrane layer.
- System Cleansing: Sometimes, it’s required to clean up the system by flushing out gathered pollutants making use of a cleaning solution or by just running water through it for extended durations.
While these tasks might seem complicated, they are critical for keeping ideal efficiency. Overlooking filter replacement can lead to lowered water high quality and increased danger of system failure. It’s likewise vital to keep an eye on system pressure assesses regularly as reduced stress can show stopped up filters or membranes.
In addition, some individuals locate it testing to perform these jobs as a result of lack of technological competence or time restrictions. Several manufacturers supply straightforward designs with instinctive user interfaces that simplify upkeep processes. Furthermore, some systems include integrated sensing units that alert customers when maintenance is needed, making it less complicated for non-technical individuals to handle their RO systems successfully.
Regardless of these challenges, several users locate the advantages of using an RO system far exceed its disadvantages. For example, enhanced water top quality is a significant benefit as RO systems can get rid of as much as 99% of contaminants from drinking water, making it much safer for intake. It’s crucial for individuals to evaluate these advantages against their certain requirements and situations prior to determining whether an RO system is right for them.
For those curious about finding out more regarding how reverse osmosis works and its layout summary, I suggest looking into this thorough post on reverse osmosis representations. This resource gives an in-depth take a look at the procedure and its different parts, aiding customers much better recognize just how these systems function.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Semi-permeable Membrane | A thin layer of product that permits water particles to travel through while obstructing larger particles and impurities. |
| Pump | Made use of to increase pressure on the feed water side of the membrane, requiring water via the semi-permeable layer. |
| Pre-treatment Systems | Filters or various other gadgets used to remove bigger fragments and contaminants prior to they get to the semi-permeable membrane. |
Understanding these elements is important for valuing both the efficiency and constraints of reverse osmosis systems. By recognizing these obstacles and taking positive actions towards maintenance, users can optimize their financial investment in these systems while enjoying cleaner, safer alcohol consumption water.
As somebody that has actually spent years researching numerous modern technologies, I can attest that reverse osmosis systems provide unequaled advantages when effectively managed. It’s necessary for users to remain watchful regarding their maintenance requirements and remain educated about improvements in technology that can even more enhance their experience with these systems.

** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Designer **: “Reverse osmosis resembles a filter that uses stress to push water with a membrane layer, dividing pollutants from distilled water.”
XI. Real-Life Instances: How Reverse Osmosis Functions (Representation Summary)
A. Desalination Plants
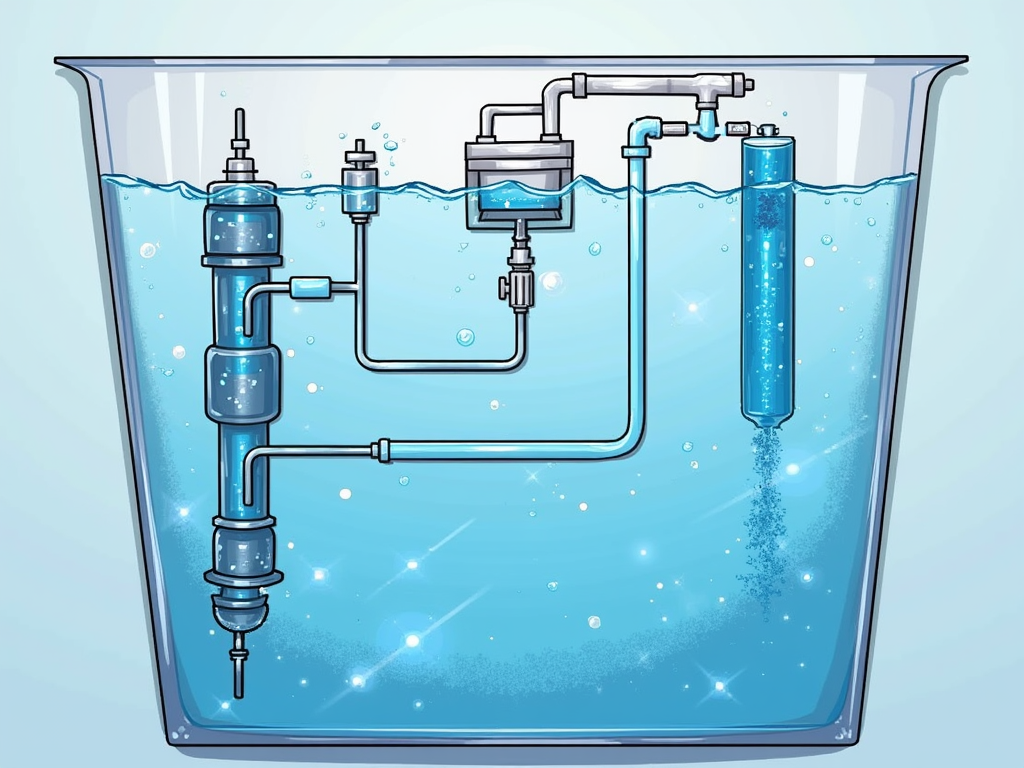
Desalination plants are an archetype of where reverse osmosis (RO) technology beams. These plants use RO to get rid of salt and various other minerals from seawater, making it drinkable. The procedure involves requiring seawater via semi-permeable membrane layers, which filter out the impurities. This method is crucial for providing clean alcohol consumption water in seaside areas where typical water resources are limited. The desalination plant in Ras Al Khair, Saudi Arabia, utilizes RO to generate over 1 million cubic meters of freshwater daily.
B. Water Purification Equipments
Water filtration systems also heavily count on RO modern technology. These systems are designed to eliminate contaminants like bacteria, infections, and dissolved solids from faucet water. The basic principle continues to be the very same: applying pressure to press water through a semi-permeable membrane that filters out contaminations. This guarantees that household water is safe for usage. For instance, lots of home filtering systems integrate RO technology to provide tidy drinking water at a cost effective expense.
Allow’s dive deeper right into exactly how this procedure collaborates with a layout summary:
| Tip | Summary |
|---|---|
| 1. Pre-treatment | Eliminates bigger bits like sediment and particles from the water. |
| 2. High Stress Application | Forces water via a semi-permeable membrane layer under high pressure. |
| 3. Filtration | The semi-permeable membrane strain impurities like salt, bacteria, and viruses. |
| 4. Post-treatment | Adds disinfectants or various other chemicals to make sure full filtration. |
Here’s a detailed break down making use of bullet points:
- Pre-treatment: This action entails removing bigger fragments like debris and particles from the water using techniques such as coagulation or sedimentation.
- High Pressure Application: The water is then based on high pressure to push it through a semi-permeable membrane.
- Filtering: The semi-permeable membrane layer strain pollutants like salt, microorganisms, and infections based upon their size and charge.
- Post-treatment: Ultimately, anti-bacterials or various other chemicals might be added to guarantee total filtration of the water.
For those curious about finding out more regarding this process, I recommend checking out this short article on how reverse osmosis works. It supplies a comprehensive check out both theoretical and functional applications of RO modern technology.
As someone that has spent years researching sophisticated modern technologies like reverse osmosis, I can attest that recognizing these systems is important for appreciating their influence on our everyday lives. Whether it’s ensuring tidy alcohol consumption water or supporting commercial procedures requiring pure fluids, RO innovation stays an unrecognized hero behind numerous contemporary comforts.
Following time you turn on your faucet and appreciate crystal-clear water without any worries about impurities bear in mind that there’s even more than satisfies the eye at play here The complex dance between stress forces and molecular filters makes sure that every decline satisfies stringent quality standards before reaching your glass.
And if you ever before locate on your own asking yourself exactly how such complicated processes become so smooth in everyday life just consider all those behind-the-scenes efforts taking place right under our noses From desalination plants transforming sea waves into life-giving streams to home filters making faucet water safe for intake each step relies heavily on concepts rooted deep within scientific questions.
Right here’s to commemorating these unsung heroes of contemporary design: might their technologies continue inspiring future generations as they strive towards creating far better worlds one molecule at a time!
** “Reverse osmosis resembles a filter for your water, just like just how a cook utilizes a fine-mesh sieve to separate the best active ingredients,”** – Chef Emma Thompson
XII. Verdict
In this detailed guide, we have actually explored the intricacies of reverse osmosis (RO), discovering its standard concepts, essential components, and real-life applications. By recognizing how reverse osmosis works, you can appreciate the significance of this innovation in making certain clean drinking water and industrial purification.
The journey began with an introduction to what turn around osmosis is and why it’s crucial to comprehend its systems. We then dived into the standard principles behind RO, highlighting the semi-permeable membrane and pressure application that drive the filtering process.
The procedure itself includes pre-treatment actions to get rid of pollutants before water flows via the membrane layer module under high pressure. This strenuous filtering makes certain that only pure water particles travel through while contaminants are denied.
An important facet of RO systems is their essential elements: high-pressure pumps, membrane modules, and post-treatment phases. Each component plays an essential function in preserving efficiency and effectiveness.
The representation review supplied a graph of these key elements, making it much easier to comprehend how water streams with the membrane layer. This area additionally described osmosis vs reverse osmosis, highlighting how water particle activity differs between these two processes.
We also talked about variables impacting efficiency such as pressure degrees and membrane layer top quality. These variables are essential in establishing the overall efficiency of an RO system.
Common applications consist of home use for house filtering systems as well as industrial filtration for massive procedures like desalination plants.
The advantages and advantages of using RO innovation consist of improved water top quality and economical services for both domestic and industrial requirements.
There are challenges and limitations connected with RO systems including energy consumption and upkeep demands.
Real-life instances such as desalination plants demonstrate the useful application of RO technology in developing tidy drinking water from seawater or brackish water sources.
- Comprehending SemiPermeable Membrane: Vital for removing impurities.
- Stress Application: Important in driving water particles with the membrane.
- PreTreatment Steps: Necessary to eliminate larger impurities prior to purification.
- HighPressure Pump: Makes sure consistent flow rate throughout filtering.
- Membrane layer Module: The heart of any kind of RO system where actual filtering occurs.
- PostTreatment Phase: Added actions taken after filtering to make sure final pureness.
- Representation Review: Graph helping comprehend complicated procedures easily.
- Osmosis vs Reverse Osmosis: Recognizing movement differences between two procedures.
- Elements Affecting Effectiveness: Stress degrees & membrane layer quality essential for efficiency.
- Usual Applications: Home use & commercial filtration including desalination plants.
- Advantages & Advantages: Better water high quality & affordable services offered.
- Difficulties & Limitations: Power consumption & maintenance demands need consideration.
In final thought, comprehending just how reverse osmosis jobs is important for valuing its duty in ensuring clean drinking water and commercial purification processes. By realizing these principles with comprehensive explanations and aesthetic help like representations, you can better value the technology behind RO systems.
Whether you’re wanting to apply an RO system in the house or discovering its industrial applications, this guide has offered you with thorough insights into its operations and importance in modern times.
Thanks for joining us on this journey via the world of reverse osmosis We hope you located this details interesting and helpful.
For more detailed information or more questions about reverse osmosis systems or any kind of various other related subjects really feel cost-free to contact us
FAQ: How reverse osmosis jobs (representation summary)
1. What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water filtration procedure that uses pressure to compel water with a semi-permeable membrane, removing pollutants and pollutants.
2. What is the Function of Reverse Osmosis?
The key purpose of reverse osmosis is to produce tidy alcohol consumption water by removing dissolved solids, germs, viruses, and various other impurities from raw water.
3. Exactly How Does Opposite Osmosis Job?
Reverse osmosis jobs by applying pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane. This membrane has little pores that allow water molecules to pass with however block larger fragments like salts and minerals.
4. What Are the Secret Elements of a Reverse Osmosis System?
The crucial parts consist of a pre-filter to remove larger bits, the semi-permeable membrane layer, and a post-filter to polish the detoxified water.
5. What Occurs During the Reverse Osmosis Process?
Throughout the process, raw water is forced with the semi-permeable membrane under stress. Contaminations are declined by the membrane and flushed out as waste, while clean water goes through.
6. Just How Does Pressure Play a Function in Reverse Osmosis?
Stress is vital backwards osmosis as it pushes the water through the semi-permeable membrane against its all-natural circulation direction (osmosis), enabling pollutants to be gotten rid of.
7. What Are Some Common Applications of Reverse Osmosis?
Typical applications include household water filtration systems, industrial procedures calling for high-purity water (e.g., drugs), and salt water desalination plants.
8. Just How Reliable Is Opposite Osmosis in Eliminating Pollutants?
Reverse osmosis can get rid of up to 99% of dissolved solids and various other impurities from raw water, making it highly efficient for producing clean alcohol consumption water.
9. What Are Some Limitations of Reverse Osmosis Equipments?
Limitations consist of power intake as a result of the need for high pressure, possibility for membrane layer fouling otherwise appropriately kept, and restricted capability for dealing with high volumes of water.
10. Just how Do You Preserve a Reverse Osmosis System?
Upkeep involves regular substitute of filters (pre-filter and post-filter), cleansing or changing the semi-permeable membrane layer as needed, and making sure proper installment and positioning of elements.
11. Can Reverse Osmosis Eliminate All Sorts Of Impurities?
While reverse osmosis is very efficient versus liquified solids and several natural substances, it may not eliminate all kinds of impurities such as specific gases or particular sorts of germs that are not affected by stress alone.
12. Is Reverse Osmosis Ecologically Friendly?
Reverse osmosis can be eco-friendly if appropriately managed; nevertheless, improper disposal of waste created throughout the procedure can present ecological dangers otherwise managed properly.

Dr. Tina M. Nenoff is a senior scientist and Sandia Fellow at Sandia National Laboratories, renowned for her pioneering work in nanoporous materials. Her research focuses on the chemistry of confinement and reactivity of ions and molecules within these materials, leading to significant advancements in environmental remediation and energy applications. Notably, she played a crucial role in developing crystalline silicotitanates used to remove radioactive cesium from contaminated seawater following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.

