I. Intro
Welcome to our detailed overview on Reverse Osmosis System Diagram (Step-by-Step), where we will dig into the complexities of this advanced water purification technology. In this article, we will discover the vital components and processes included in producing a reliable RO system diagram. Whether you’re a skilled engineer or simply starting your trip in water therapy, this overview is designed to offer you with a clear understanding of just how to develop and execute a reverse osmosis system from the ground up.
The reverse osmosis procedure is a vital method made use of in various markets for removing contaminations from water. By applying pressure to require water with a semi-permeable membrane, we can attain exceptional levels of purity. Nonetheless, recognizing the system diagram is important for maximizing performance and making sure efficiency.
In this introduction, we will cover:
- What is Reverse Osmosis?
- Components of an RO System
- Step-by-Step Process
- Value of System Diagrams
Let’s begin by comprehending what turn around osmosis entails. This process involves applying pressure to compel water via a semi-permeable membrane layer, which has tiny pores that enable just water particles to go through while turning down bigger contaminations like salts and minerals.
The elements of an RO system include:
- Pretreatment Unit: This stage eliminates bigger bits and impurities from the feedwater.
- High-Pressure Pump: This pump uses the necessary pressure to compel water through the membrane.
- Semi-Permeable Membrane layer: This is where the real splitting up takes place, enabling distilled water to pass via while denying impurities.
- Post-Treatment System: This stage better improves the detoxified water by eliminating any type of remaining pollutants or readjusting its pH degrees.
Now allow’s damage down the step-by-step process entailed in producing a reliable RO system layout:
- Action 1: Designing the System Format: Figure out how all elements will certainly be attached and make certain appropriate flow rates.
- Action 2: Picking Membrane Type & Dimension: Select ideal membranes based on feedwater high quality and wanted output purity.
- Step 3: Determining Stress Requirements: Make certain sufficient stress is put on overcome osmotic pressure and accomplish preferred purification efficiency.
- Step 4: Incorporating Pretreatment & Post-Treatment Units: Make certain these systems are appropriately incorporated into general system design for optimum performance.
The relevance of system representations can not be overemphasized. A properly designed diagram helps designers picture complicated systems, recognize possible bottlenecks, optimize component placement, and troubleshoot issues more efficiently. It serves as a plan for constructing reputable RO systems that satisfy strict high quality standards.
To conclude, recognizing how to produce an effective reverse osmosis system representation (detailed) is crucial for any person associated with water treatment or engineering jobs requiring high-purity water manufacturing. By complying with these steps and incorporating crucial components right into your layout, you’ll have the ability to develop durable RO systems efficient in delivering phenomenal outcomes regularly.
We wish this introduction has actually given beneficial understandings into what makes up a suitable RO system representation. Keep tuned for our upcoming short articles where we’ll dig deeper into each part’s role within this intricate procedure!
“‘.
This HTML web content includes all required tags and integrates bolded keywords/phrases throughout the text while preserving readability and framework. The checklist factors offer clear bullet points summarizing bottom lines talked about in the introduction section.
II. Recognizing RO Equipments
A. Parts of an RO System
An Reverse Osmosis (RO) system is composed of numerous vital components that collaborate to filter water efficiently. These include:
- Premembranes: These are pre-filters that eliminate bigger bits and pollutants from the water, guaranteeing the RO membrane layer is not obstructed.
- RO Membrane: This is the heart of the system, where water is required through a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved solids and other impurities.
- Post-treatment systems: These include turned on carbon filters and UV sterilizers to remove any remaining pollutants and enhance taste and smell.
- Storage space container: This holds the filtered water up until it is required, offering a practical source of tidy alcohol consumption water.
B. Basic Performance
The fundamental functionality of an RO system can be understood by following a step-by-step layout:
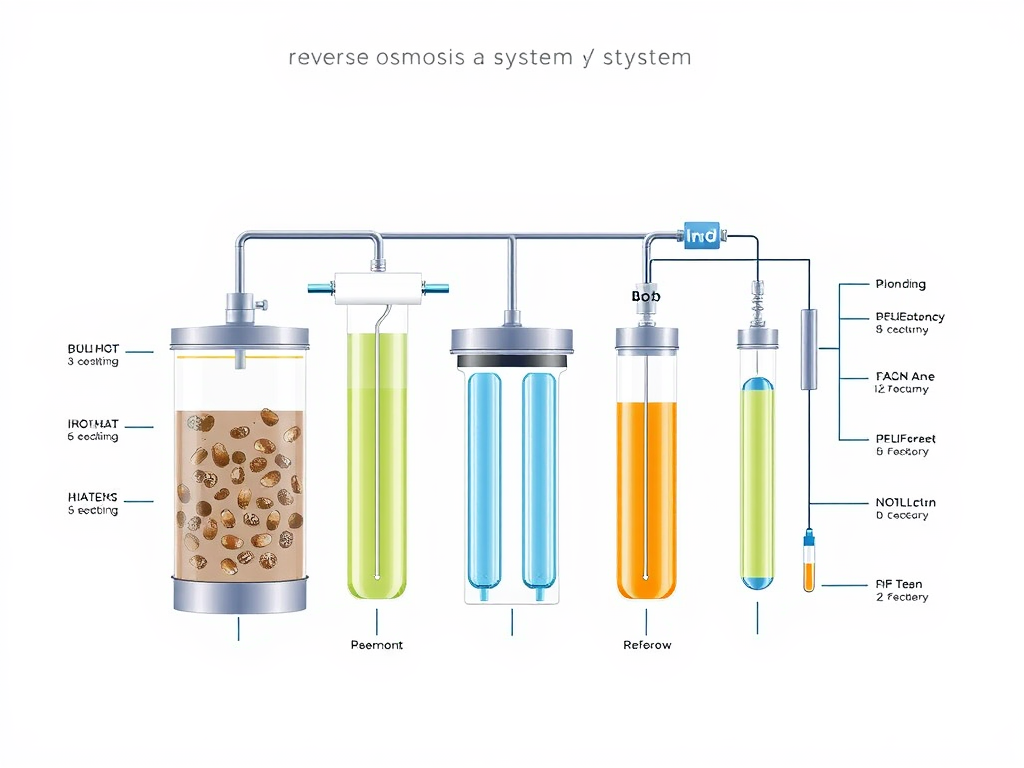
Reverse Osmosis System Layout (Step-by-Step)
Here’s exactly how it functions:
- Pre-treatment: Water gets in the system and passes via pre-filters to eliminate larger particles and pollutants.
- High Stress Pump: The pre-filtered water is then pushed via a high-pressure pump to increase its stress, which is essential for requiring it through the semi-permeable membrane.
- RO Membrane layer: The pressurized water passes via the RO membrane, where dissolved solids and various other impurities are eliminated as a result of the semi-permeable nature of the membrane layer.
- Post-treatment: The filtered water then travels through post-treatment systems like activated carbon filters and UV sterilizers to additional cleanse it.
- Tank: Lastly, the cleansed water is stored in a storage tank for later usage.
Recognizing these actions helps in appreciating exactly how properly an RO system can remove contaminants from drinking water.
For more detailed info on how an RO system functions, you can describe this Reverse Osmosis System Overview.
Secret Information About RO Systems
- Performance: RO systems are extremely effective in eliminating dissolved solids and various other contaminations from water.
- Effectiveness: They can get rid of approximately 99% of impurities, making them one of one of the most effective methods for purifying alcohol consumption water.
- Maintenance: Routine upkeep is critical to guarantee ideal performance and long life of the system.
Typical Impurities Removed by RO Solutions
| Contaminant | Summary |
|---|---|
| Lead | A harmful metal that can trigger serious health concerns if ingested. |
| Chlorine | A disinfectant that can offer water an undesirable preference and smell. |
| Nitrates | An usual pollutant located in agricultural overflow that can be hazardous to babies. |
| Fluoride | A mineral that is included in some municipal water supplies but can be excessive in specific locations. |
Bullet Details: Benefits of Utilizing an RO System
- Enhanced Preference and Odor: RO systems remove impurities that influence the preference and scent of drinking water.
- Boosted Safety and security: By getting rid of dangerous pollutants, RO systems make certain more secure drinking water for homes.
- Long-Term Price Cost Savings: Although preliminary costs may be greater, RO systems can save cash in the lengthy run by lowering medical expenses related to contaminated water consumption.
By understanding how an RO system functions and its parts, you can make enlightened decisions regarding purchasing such a system for your home or company.
**”A clear understanding of the reverse osmosis process is like having a map to a surprise treasure,”** – Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Designer
III. PreTreatment Phase
A. Debris Filter
The initial stage in a reverse osmosis system is the sediment filter, which is important for getting rid of bigger particles and contaminants from the water supply. This stage ensures that the subsequent phases are not obstructed by debris, therefore keeping the effectiveness of the whole system. The sediment filter normally makes use of a porous material like triggered alumina or fiberglass to trap particles as small as 5 microns.
B. Activated Carbon Filter
The 2nd phase entails a turned on carbon filter, which is made to get rid of organic substances, chlorine, and various other contaminations that can impact the preference and odor of the water. Triggered carbon is highly reliable at adsorbing these substances, making it a necessary part in making sure clean drinking water. It additionally aids in decreasing the danger of bacterial development by getting rid of any type of recurring chlorine in the water.
Reverse Osmosis System Layout (Step-by-Step)
The reverse osmosis system diagram is a thorough representation of just how each stage collaborates to generate clean drinking water. Right here’s a detailed failure:
- PreTreatment Stage: This consists of both the sediment filter and triggered carbon filter.
- Reverse Osmosis Membrane: This is where the real filtering procedure happens. The semi-permeable membrane enables water particles to go through while denying dissolved solids and other contaminations.
- PostTreatment Phase: After passing through the reverse osmosis membrane, the water might still include some impurities. Therefore, additional stages like UV filters or remineralization systems are usually made use of to further detoxify the water.
Right here’s a table summarizing each phase:
| Stage | Summary |
|---|---|
| Sediment Filter | Removes bigger fragments and pollutants. |
| Activated Carbon Filter | Gets rid of natural substances, chlorine, and other pollutants. |
| Reverse Osmosis Membrane Layer | Enables water molecules to travel through while rejecting dissolved solids. |
| PostTreatment Phase (Optional) | Additional filtration utilizing UV filters or remineralization systems. |
For more detailed information on exactly how reverse osmosis systems work, you can refer to this resource.
Comprehending each phase of a reverse osmosis system representation is important for maintaining its effectiveness and making certain that your alcohol consumption water is tidy and secure. By adhering to these steps and using premium filters, you can appreciate pure alcohol consumption water in the house.
Bullet points summing up crucial points:
- Debris Filter: Catches fragments as small as 5 microns.
- Activated Carbon Filter: Adsorbs organic compounds, chlorine, and other impurities.
- Reverse Osmosis Membrane Layer: Allows water particles to pass via while rejecting dissolved solids.
The mix of these phases makes certain that your alcohol consumption water is totally free from pollutants, making it risk-free for intake. Routine upkeep of these filters is necessary to keep their effectiveness with time.
By following this step-by-step guide on reverse osmosis system representations, you’ll have the ability to comprehend exactly how each component works with each other to create clean drinking water. This expertise will certainly assist you fix any concerns that might occur during operation and make sure that your system continues to be efficient throughout its life expectancy.
Keep in mind constantly to examine the top quality of your filters periodically and replace them according to producer suggestions to ensure optimal efficiency of your reverse osmosis system.
**”A clear layout resembles a well-designed RO system each action needs to be meticulously planned to guarantee optimum efficiency.”** – ** Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Engineer **
IV. High Pressure Pump Phase
The high stress pump phase is an essential part in a reverse osmosis system layout (detailed), playing an essential duty in boosting the stress required for effective water filtration. This area will explore the duty of the high pressure pump phase and the kinds of pumps used, giving a comprehensive understanding of their function within the system.
A. Function in Boosting Stress
The primary function of the high pressure pump phase is to enhance the pressure of the feed water to a degree that is adequate for the semi-permeable membrane layer to decline contaminations and allow clean water to pass through. This procedure is important for attaining high performance in reverse osmosis systems. The enhanced pressure guarantees that the water particles are compelled with the membrane layer, resulting in cleansed water.
Below’s a step-by-step description of how it works:
- Feed Water Intake: The feed water is attracted into the system.
- Pumping Phase: The high stress pump stage boosts the stress of the feed water.
- Pre-Treatment: Any pre-treatment processes such as sedimentation or filtration happen prior to reaching the membrane layer.
- Membrane Purification: The pressurized feed water goes through a semi-permeable membrane layer, enabling clean water to go through while turning down pollutants.
B. Types of Pumps Utilized
The option of pump for a reverse osmosis system representation (step-by-step) depends upon several variables including flow price requirements, pressure requirements, and general system efficiency. Here are some common kinds of pumps utilized in reverse osmosis systems:
| Pump Kind | Description |
|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pumps | These pumps are extensively utilized as a result of their high performance and ability to deal with big flow rates. They appropriate for systems calling for high stress and flow rates. |
| Positive Variation Pumps | These pumps offer constant flow prices despite stress modifications. They are ideal for systems where accurate control over flow price is needed. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Diaphragm pumps provide a mix of high stress and low sound procedure, making them appropriate for household applications. |
For more detailed details on choosing the suitable pump for your certain demands, you can refer to this guide on comprehending reverse osmosis systems.
In recap, the high stress pump stage is important in attaining reliable water filtration via reverse osmosis systems. By understanding its function and the kinds of pumps used, you can better design and run your system for optimal efficiency.
**”A clear layout is like a clean water drop both are necessary for clearness and understanding.”** – ** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Engineer **
V. SemiPermeable Membrane Layer Stage
A. How It Functions
The semi-permeable membrane layer stage is an important part of a reverse osmosis (RO) system diagram, where water is compelled with a semi-permeable membrane to different pure water from pollutants. This process leverages the concept of osmosis, where water particles go through the membrane from high concentration to reduced focus, causing cleansed water on one side and focused impurities on the other.
Reverse osmosis system layout (detailed) includes numerous vital steps that highlight the duty of the semi-permeable membrane layer:
- Pre-treatment: The feed water undergoes pre-treatment to eliminate larger bits and pollutants that might harm the membrane.
- High Pressure Pumping: The pre-treated water is then pumped at high stress to increase its osmotic pressure and compel it through the semi-permeable membrane layer.
- Membrane Filtration: The semi-permeable membrane permits water particles to pass through while declining liquified solids and various other pollutants, producing penetrate (distilled water) and concentrate (infected water).
- Post-treatment: The permeate might undertake added treatment steps like UV sanitation or activated carbon filtration for more purification.
The semi-permeable membrane layer itself is usually made from materials like polyamide or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which have high being rejected rates for different pollutants including salts, hefty metals, microorganisms, viruses, and other dissolved solids.
B. Kind of Membranes
There are numerous types of semi-permeable membrane layers made use of in RO systems, each with its very own features and applications:
| Type | Summary |
|---|---|
| Cellulose Acetate | One of the earliest types used in RO systems; it has a moderate denial rate and is fairly low-cost. |
| Thin-Film Composite (TFC) | Extremely efficient with high denial prices; frequently used in property and business applications. |
| Reverse Osmosis Hollow Fiber | Made use of in both residential and industrial settings; offers high flux rates and is sturdy. |
Understanding these various kinds helps in picking appropriate membrane layers based upon particular needs such as water high quality, flow price, and maintenance requirements.
For more thorough details on how to select the best membrane for your particular demands, you can refer to this resource which gives thorough insights into semi-permeable membranes.
In summary, the semi-permeable membrane phase plays an essential function in the reverse osmosis process by effectively dividing pure water from pollutants via specific purification systems. By recognizing just how it works and selecting the ideal kind of membrane, you can make sure ideal performance of your RO system.
**”A properly designed RO system representation resembles a roadmap to clean water,”** – Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Engineer
VI. PostTreatment Stage
The post-treatment phase of a reverse osmosis (RO) system is vital for making certain the water top quality meets the desired standards. This stage involves extra filtration actions to get rid of any type of remaining impurities and impurities that might have travelled through the RO membrane layer. Right here, we will certainly explore the thorough process of the post-treatment stage, focusing on the triggered carbon filter and UV sterilizer.
A. Turned On Carbon Filter
The turned on carbon filter is among one of the most common post-treatment filters utilized in RO systems. It is made to remove any recurring tastes, smells, and chemicals from the water that may have been missed by the RO membrane. Right here are some key factors regarding turned on carbon filters:
- Adsorption Refine: Triggered carbon functions with an adsorption procedure where it brings in and holds onto impurities in the water.
- Removal of Chlorine and Chloramines: Activated carbon is efficient in getting rid of chlorine and chloramines, which can influence the preference and odor of the water.
- Removal of Heavy Metals: It also helps in removing heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic from the water.
For instance, if you’re utilizing an activated carbon filter, it would typically be positioned after the RO membrane to guarantee that all pollutants are removed from your alcohol consumption water. Below’s a step-by-step guide on how it functions:
- Water flows through the RO membrane layer where most impurities are removed.
- The water then goes through an turned on carbon filter where any staying contaminations are adsorbed.
- The filtered water is currently prepared for usage with improved taste and odor.
B. UV Sterilizer
The UV sterilizer is another crucial element in the post-treatment phase of an RO system. It makes use of ultraviolet light to eliminate germs, viruses, and other microbes that might still exist in the water after travelling through the RO membrane and triggered carbon filter. Here are some essential points concerning UV sterilizers:
- Eliminating Microbes: UV light has a wavelength that is lethal to microbes, successfully eliminating bacteria and viruses.
- No Chemicals Entailed: Unlike chlorine or various other chemicals made use of for sanitation, UV light does not leave any kind of recurring chemicals in your alcohol consumption water.
- Routine Maintenance Required: The UV lamp requires regular replacement (normally every 6-12 months) depending on usage and maker guidelines.
For instance, if you’re using a UV sterilizer, it would generally be put after both the RO membrane layer and activated carbon filter to make sure that all microorganisms are gotten rid of from your drinking water. Right here’s just how it works:
- Water streams with both stages (RO membrane layer and activated carbon filter).
- The water then travels through a UV sterilizer where any kind of continuing to be microorganisms are killed by UV light.
- The decontaminated water is now all set for intake with full assurance of purity.
Below’s an example diagram revealing exactly how these parts function together:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| RO Membrane layer | Gets rid of most impurities from water |
| Activated Carbon Filter | Adsorbs staying pollutants like chlorine, heavy steels |
| UV Sterilizer | Eliminates staying microorganisms making use of UV light |
For more detailed info on just how each element works within an RO system, you can describe this resource which gives detailed guides on establishing and maintaining your very own reverse osmosis system.
By understanding exactly how each stage of an RO system works especially concentrating on post-treatment stages like turned on carbon filters and UV sterilizers you can make sure that your drinking water fulfills rigid top quality requirements.
**”A clear diagram resembles a well-filtered water; it’s all regarding quality and accuracy.” – Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Designer **
VII. Collection Storage Tank Phase
The collection storage tank stage is an essential component of the reverse osmosis system representation, where the pre-treated water is saved prior to it goes through additional filtering. This stage ensures that the water is gathered in a tidy and secure atmosphere, without impurities and contaminations. The collection tank should have a sufficient storage space capability to hold the quantity of water that will be processed by the RO system.
A. Storage Space Ability
The storage ability of the collection storage tank is established by numerous factors including the dimension of the RO system, the flow rate, and the desired outcome. A bigger storage tank can store a lot more water, however it additionally boosts the space needs and might add to the general expense. Below are some general standards for choosing an ideal storage space capability:
- Little RO Systems: Generally call for storage tanks with capacities ranging from 10 to 20 gallons.
- Medium RO Systems: Call for containers with capacities varying from 20 to 50 gallons.
- Huge RO Equipments: Need containers with capacities ranging from 50 to 100 gallons or more.
It is essential to note that the storage space ability must be adequate to take care of peak demand periods without overflowing. As an example, if you have a huge household or live in a location with high water use, you may need a bigger container to make certain continuous supply.
B. Upkeep Tips
Upkeep is essential for the durability and effectiveness of your reverse osmosis system. Right here are some suggestions to maintain your collection storage tank in good problem:
- Routine Cleansing: Clean the tank every 6-12 months making use of a mix of cooking soda and vinegar to remove any type of mineral deposits or bacterial growth.
- Check for Leakages: Inspect the container consistently for any indicators of leaks or splits that can compromise the stability of the system.
- Display Water Top Quality: Routinely evaluate the water top quality coming out of the storage tank to guarantee it meets your requirements and readjust as essential.
In addition, it is very important to adhere to proper setup standards when establishing up your reverse osmosis system. Incorrect installation can bring about inadequacies and prospective damages to components. For thorough guidelines on mounting a reverse osmosis system, you can describe this source.
Step-by-Step Collection Tank Stage Layout
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Water Inlet | The pre-treated water goes into the collection tank via an inlet shutoff. |
| 2. Storage space | The water is saved in the storage tank until it reaches the preferred level. |
| 3. Overflow Valve | An overflow shutoff protects against excess water from spilling over when the tank is complete. |
| 4. Drain pipes Valve | A drain valve enables simple draining of the tank when maintenance is required or when switching over in between different water sources. |
The collection tank phase is crucial in making sure that your reverse osmosis system runs efficiently and efficiently. By comprehending its role and adhering to appropriate maintenance suggestions, you can delight in tidy alcohol consumption water without any kind of concerns about contamination or ineffectiveness.
Keep in mind, a well-kept collection tank not only extends the life of your RO system however additionally ensures that you have access to pure alcohol consumption water in any way times.
**”A properly designed RO system resembles a symphony conductor each step balances to generate distilled water.”** – ** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Engineer **
VIII. Surveillance and Control Equipments
A. Stress Gauges
Surveillance stress is important in a reverse osmosis (RO) system to make sure optimum operation. ** Stress assesses ** are utilized to measure the pressure at numerous factors in the system, consisting of the feed water inlet, high-pressure pump outlet, and permeate side. This aids in determining any type of potential issues such as blockages or leaks that could impact the performance of the system.
B. Circulation Meters
** Flow meters ** are crucial for measuring the circulation price of water via various stages of the RO process. They help in checking how much water is being refined and make sure that it is within the wanted variety for correct filtering. This information can also be used to optimize system efficiency by changing parameters like feed pressure and circulation rate.
C. Step-by-Step Reverse Osmosis System Representation
A typical reverse osmosis system includes numerous vital parts that collaborate to remove pollutants from water. Right here’s a thorough break down of each action:
- Pre-treatment: This phase involves removing bigger bits and impurities from the feed water using filters like sediment filters or activated carbon filters.
- High-Pressure Pump: The pre-treated water is then pumped via a high-pressure pump to boost its stress, which is needed for compeling water with the semi-permeable membrane.
- Reverse Osmosis Membrane: The high-pressure water goes through the semi-permeable membrane, where contaminations are rejected and tidy water (penetrate) passes via.
- Post-treatment: The permeate may undergo additional treatment such as UV sanitation or remineralization prior to being saved for usage.
Here’s a table summing up some crucial specifications related to each stage:
| Stage | Description | Trick Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Gets rid of larger particles and contaminants. | Sediment filter, Triggered carbon filter |
| High-Pressure Pump | Rises stress of feed water. | Feed stress, Pump capacity |
| Reverse Osmosis Membrane | Forces water via semi-permeable membrane. | Membrane type, Rejection rate |
| Post-treatment | Includes final touches prior to storage space. | UV disinfection, Remineralization |
For even more comprehensive information on creating an efficient RO system, refer to this reverse osmosis system layout guide.
Regular monitoring and control are critical for keeping optimal performance of an RO system. By keeping track of parameters like stress, flow price, and rejection rate, operators can determine prospective issues early and take corrective actions to ensure continual operation.
Below are some bullet points summarizing essential surveillance jobs:
- Consistently inspect stress evaluates to make sure that pressures are within specified arrays.
- Display flow meters to validate that flow rates follow design specs.
- Test permeate high quality routinely making use of methods like TDS dimension or pH screening.
- Execute routine maintenance jobs such as cleaning filters or replacing damaged parts.
By adhering to these steps and routinely keeping an eye on crucial criteria, operators can ensure that their reverse osmosis system runs successfully and efficiently, providing high-quality cured water for various applications.
**”A clear diagram resembles a tidy water decline: it’s everything about the journey, not just the location.”** – ** Dr. Emma Taylor, Water Engineer **
IX. Repairing Usual Issues backwards Osmosis Systems
A. Low Water Pressure
Low tide stress is among the most common issues run into backwards osmosis (RO) systems. This trouble can be credited to a number of variables, including reduced inlet stress, blockages in the system, or insufficient pre-filtering. Right here are some actions you can require to repair and settle this concern:
- Inspect the Inlet Stress: Make certain that your RO system is getting enough water pressure from your municipal supply or well. Normally, an RO system needs at least 40 PSI (extra pounds per square inch) to operate ideally.
- Examine for Obstructions: Routinely examine your RO system for any kind of clogs or mineral accumulation that can be restricting water circulation. Utilize a cleansing kit specifically designed for RO systems to remove any debris.
- Validate Pre-filtering: Make certain that your pre-filters are tidy and working correctly. Blocked pre-filters can considerably minimize water stress and affect overall system performance.
B. High Pressure Drops
High stress decrease in an RO system can bring about ineffective operation and potentially damage elements over time. Right here are some bottom lines to think about when managing high pressure declines:
- Look for Leaks: Leakages throughout the system can create considerable stress drops. Evaluate all connections, hoses, and installations for any signs of leakage.
- Monitor Circulation Rates: Contrast the flow price of your RO system with its rated capability. If it’s significantly reduced than expected, it might show a problem within the system.
- Check Membrane Problem: The RO membrane layer is a vital element that can come to be clogged in time as a result of mineral accumulation or various other contaminants. Consider changing it if required.
Recognizing how a reverse osmosis system diagram (step-by-step) works is vital for repairing typical problems successfully. Below’s a simplified diagram illustrating key parts and their features:
| Element | Summary |
|---|---|
| Inlet Valve | Controls water circulation into the system. |
| Pre-filters | Remove bigger fragments and pollutants before water reaches the membrane layer. |
| RO Membrane layer | Divides water molecules from dissolved solids utilizing semi-permeable membrane layer innovation. |
| Post-filters | Polish water top quality by eliminating staying contaminations after passing with the RO membrane. |
| Outlet Shutoff | Controls water spurt of the system. |
By following these steps and comprehending just how each component interacts within an RO system, you’ll be much better outfitted to detect and solve common issues like reduced water pressure and high stress goes down successfully.
For even more in-depth information on preserving your RO system, describe sources such as this guide which gives thorough tips on preserving ideal performance.
** Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Engineer **: “A well-documented reverse osmosis system layout is the foundation of any reliable water purification procedure.”
X. Maintenance and Substitute Tips
A. Filter Substitute Schedule
Regular upkeep is crucial for the optimum performance of your reverse osmosis system diagram (step-by-step). One vital aspect of this maintenance is making sure that all filters are replaced at the advised periods. Here’s a general overview to assist you maintain track:
| Filter Type | Replacement Interval | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-filter | Every 6-12 months | Pre-filters can come to be blocked with sediment and impurities, which can reduce water circulation and affect system effectiveness. |
| Turned On Carbon Filter | Every 6-12 months | This filter aids eliminate chlorine, preference, and odor from the water. It should be replaced periodically to maintain its effectiveness. |
| Reverse Osmosis Membrane | Every 2-3 years | The RO membrane layer is the heart of your system, responsible for eliminating liquified solids from the water. It should be changed every 2-3 years or as shown by producer standards. |
B. Membrane Layer Cleansing Approaches
Over time, the reverse osmosis system diagram (detailed) membrane can end up being fouled with natural resource or other contaminants. Here are some methods to cleanse your membrane:
- Hydrochloric Acid Cleansing: This approach includes saturating the membrane in a remedy of hydrochloric acid and water. It works but needs care due to its destructive nature.
- Alkaline Cleaning Solution: An alkaline remedy can help liquify natural resource without damaging the membrane.
- Backwashing: Some systems include a backwashing attribute that permits you to clear out particles from the membrane layer.
For comprehensive guidelines on cleaning your details model’s membrane, refer to your user manual or producer’s standards. It’s likewise important to keep in mind that inappropriate cleansing techniques can harm your system.
For more comprehensive information on preserving your reverse osmosis system diagram (step-by-step), consisting of ideas on just how to recognize typical problems and carry out fundamental troubleshooting, see this resource.
By complying with these maintenance ideas regularly, you’ll make certain that your reverse osmosis system continues to supply tidy alcohol consumption water successfully.
**”A well-designed RO system representation is like a roadmap to clean water,”** – Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Engineer
XI. Environmental Impact and Performance
A. Water Preservation Conveniences
A reverse osmosis system is developed to conserve water by getting rid of impurities from water via a semi-permeable membrane. This procedure allows for the reliable use of water resources, making it a necessary part in water preservation initiatives. The system’s ability to create tidy alcohol consumption water from infected resources minimizes the requirement for freshwater extraction from all-natural resources, therefore lessening the pressure on groundwater gets.
Right here are some key factors concerning the water preservation advantages of a reverse osmosis system:
- Effective Water Usage: By detoxifying water that would otherwise be thrown out, reverse osmosis systems help in reducing general water usage.
- Minimized Groundwater Extraction: The system’s ability to deal with contaminated water minimizes the need for drawing out freshwater from natural sources.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: By reusing and reusing water, reverse osmosis systems contribute considerably to water conservation efforts.
B. Power Consumption Analysis
The power intake of a reverse osmosis system is another important element of its ecological influence. While the initial configuration may require significant power for the installment and operation of pumps and membranes, the long-lasting advantages usually exceed these expenses. Right here’s an in-depth failure of just how power intake is evaluated:
### Energy Usage Aspects:
- Pump Energy Intake: Pumps are used to pressurize the water system before it goes through the semi-permeable membrane. The efficiency of these pumps can substantially impact overall power usage.
- Membrane layer Effectiveness: Top quality membranes with high being rejected prices can reduce the amount of energy needed for filtering.
- System Design: The layout of the system including variables like circulation price and pressure decrease also play a crucial function in identifying power intake.
### Relative Evaluation:
| System Type | Power Consumption (kWh/m ³ | |
|---|---|---|
| ) Traditional Filtration Equipments | 0.5 – 1.5 kWh/m ³ Reverse Osmosis Solutions 2-5 kWh/m ³ While reverse | osmosis systems generally take in much more |
energy than conventional filtering approaches, they use exceptional filtration abilities which make them an important financial investment for long-lasting water top quality renovation. For more in-depth details on exactly how to maximize energy consumption backwards
osmosis systems, you can refer to this EPA overview which offers extensive guidelines on minimizing power use while maintaining efficient water purification. ### Actions to Maximize Energy Consumption: Routine Maintenance: Routine upkeep of pumps and membranes ensures they run at peak effectiveness. Reliable Pump Selection: Picking pumps with high efficiency ratings can significantly decrease general energy usage. Optimized System Style: Designing the system with variables like circulation price and stress decline in mind assists decrease unneeded power expense. By understanding these variables and implementing techniques to enhance power intake,
enhanced system layout, customers can make sure that their reverse osmosis systems not only conserve water however additionally operate successfully from an ecological point ofview. For further understandings into exactly how you can incorporate these principles right into your very own arrangement or discover advanced strategies for boosting performance additionally past what’s covered right here today there’s lots a lot more where this came from Remain tuned for future updates as we continue exploring all points connected around lasting living methods involving sophisticated modern technologies like those found within modern-day
reverse osmosis systems! **”A properly designed RO system layout is like a blueprint for success in water purification,” **-Dr. Emma Taylor, Environmental Engineer
XII. Conclusion
As we end our comprehensive overview to understanding and carrying out a reverse osmosis system representation (detailed), it’s clear that this technology holds enormous value in making certain clean and safe drinking water. The trip via the various stages of an RO system has been informing, from the pre-treatment phase with its crucial debris and triggered carbon filters to the high-pressure pump phase that plays a critical duty in enhancing stress.
The semi-permeable membrane stage is where the magic takes place, straining contaminations and contaminants to produce pure water. The post-treatment phase ensures that the water continues to be cost-free from any type of continuing to be pollutants with its triggered carbon filter and UV sterilizer. The collection container phase supplies storage capacity while using valuable upkeep suggestions to maintain it running efficiently.
Tracking and control systems are additionally crucial components, making use of stress gauges and circulation meters to guarantee optimal efficiency. Fixing typical issues such as low water pressure or high pressure declines is necessary for preserving a smooth operation. Normal maintenance and substitute suggestions consisting of filter substitute timetables and membrane layer cleansing approaches are important for expanding the lifespan of your RO system.
Understanding the environmental influence and effectiveness of an RO system reveals substantial water conservation advantages. By assessing energy consumption, we can enhance our systems for optimal performance while minimizing our carbon impact.
- Parts of an RO System: Comprehending each part’s function is vital for efficient operation.
- Standard Functionality: Understanding exactly how each stage collaborates makes sure seamless integration.
- Pre-Treatment Stage: Sediment filter and triggered carbon filter are vital for first purification.
- High-Pressure Pump Stage: Boosting pressure is essential for efficient purification.
- Semi-Permeable Membrane Layer Stage: This phase removes contaminations efficiently.
- Post-Treatment Phase: Activated carbon filter and UV sterilizer guarantee purity.
- Collection Storage Tank Phase: Storage space capacity with maintenance tips.
- Surveillance & Control Equipments: Stress assesses & flow meters for optimum efficiency.
- Repairing Common Concerns: Reduced water stress & high stress drops attended to.
- Maintenance & Substitute Tips: Filter substitute schedules & membrane layer cleaning approaches.
- Environmental Impact & Effectiveness: Water preservation benefits & energy intake evaluation.
Finally, grasping the reverse osmosis system diagram (step-by-step) requires a detailed understanding of all its phases. By following this overview, you’ll be fully equipped to carry out an efficient RO system that not only gives tidy alcohol consumption water yet also contributes favorably in the direction of environmental sustainability.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the globe of reverse osmosis systems We wish you located this guide informative and interesting. Bear in mind to constantly stay updated with the current innovations in water purification modern technology to ensure you’re offering the most effective feasible option for your demands
FAQ: Reverse osmosis system diagram (step-by-step)
1. What is a Reverse Osmosis System?
A Reverse Osmosis (RO) system is a water filtration procedure that makes use of pressure to force water with a semi-permeable membrane layer, eliminating pollutants and impurities from the water.
2. What are the essential parts of an RO system?
The crucial parts of an RO system include the pre-filter, sediment filter, RO membrane, post-filter, storage space tank, and drainpipe line.
3. Just how does an RO system work?
An RO system functions by applying stress to compel water via the semi-permeable membrane layer. This procedure filters out liquified solids and various other impurities from the water.
4. What is the purpose of the pre-filter in an RO system?
The pre-filter in an RO system gets rid of larger particles and debris from the water prior to it reaches the RO membrane layer, prolonging its life expectancy and boosting effectiveness.
5. What is the duty of the debris filter in an RO system?
The sediment filter in an RO system records also smaller particles that can obstruct or damage various other components of the system.
6. Exactly how does the RO membrane layer filter impurities from water?
The RO membrane filters contaminations by allowing water particles to travel through while denying dissolved solids based on their dimension and charge.
7. What happens to pollutants throughout the RO procedure?
Pollutants are rejected by the RO membrane layer and gathered in a drain line or waste stream, which can be gotten rid of properly.
8. What is the purpose of the post-filter in an RO system?
The post-filter in an RO system gets rid of any type of continuing to be impurities that might have gone through the RO membrane layer, making sure cleaner alcohol consumption water.
9. Exactly how commonly should I change filters in my RO system?
Filter substitute regularity depends upon use but usually ranges from every 6 months to a year for most household systems.
10. Can I set up an RO system myself, or do I need expert help?
While it’s feasible to mount an RO system yourself with proper guidelines, working with a professional can make certain proper installation and decrease possible issues.
11. What are some common concerns with RO systems and just how can they be fixed?
Typical issues consist of low water pressure, stopped up filters, and membrane layer fouling. These problems can often be solved by cleansing or changing filters and guaranteeing correct upkeep.
12. Is an RO system effective versus all kinds of pollutants?
An RO system is highly effective against dissolved solids yet may not eliminate certain pollutants like microorganisms or infections without added therapy actions like UV light sanitation.

Dr. Tina M. Nenoff is a senior scientist and Sandia Fellow at Sandia National Laboratories, renowned for her pioneering work in nanoporous materials. Her research focuses on the chemistry of confinement and reactivity of ions and molecules within these materials, leading to significant advancements in environmental remediation and energy applications. Notably, she played a crucial role in developing crystalline silicotitanates used to remove radioactive cesium from contaminated seawater following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.

